
Business Cases in SAP S/4HANA Projects
In the era of constant technological advancement, businesses are faced with the pressing need to adapt and innovate to stay competitive. SAP S/4HANA, an enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution, has emerged as a game-changer, enabling organizations to embrace digital transformation and gain a strategic edge. However, to ensure successful implementation and utilization of SAP S/4HANA, thorough evaluation and strategic planning are imperative. This is where Business Cases play a pivotal role.
In this context, Business Cases serve as comprehensive and data-driven analyses that assess the feasibility, benefits, risks, and costs of SAP S/4HANA projects. They form the bedrock of decision-making, providing stakeholders with valuable insights and substantiating the value proposition of the initiative. By carefully evaluating financial viability, potential challenges, and long-term impacts, Business Cases enable organizations to make informed choices that align with their broader objectives. The creation of solid business cases is the foundation for successful SAP S/4HANA projects.
Prerequisites and Cost Analysis
Prerequisites and cost analysis are crucial for the success of SAP S/4HANA projects. The business case serves as the project’s foundation, outlining objectives, scope, and justification for investment. It aligns stakeholders, secures buy-in, and ensures project alignment with strategic goals.
Cost analysis evaluates project financial feasibility, considering initial investment and ongoing operational costs. Decision-makers assess ROI and identify cost optimization opportunities to enhance efficiency and achieve cost savings. Through a well-structured business case and comprehensive cost analysis, organizations pave the way for a successful SAP S/4HANA project that drives transformative outcomes.
Cost Calculation and ROI
Calculating ROI for SAP S/4HANA projects can be complex due to various factors. Organizations must consider not only the direct financial benefits but also the indirect and intangible impacts on operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and competitiveness. Additionally, the evaluation should encompass potential risks and complexities associated with the implementation, such as technical challenges, data migration issues, and potential disruptions during the transition phase.
To provide a comprehensive view of the financial aspects, Business Cases for SAP S/4HANA projects include a breakdown of cost blocks. These cost blocks categorize the different types of expenses associated with the project:
- One-off costs: These are initial expenses incurred during the implementation phase, such as software licensing, hardware procurement, consulting fees, and training.
- Running costs: These represent ongoing operational expenses post-implementation, including maintenance, support, licensing renewals, and staff salaries related to managing the SAP S/4HANA system.
- Other costs not necessarily related to IT: These costs might not be directly tied to IT but can impact the project, such as process redesign, organizational change management, and compliance-related expenses.
A comprehensive breakdown of these cost blocks enables organizations to identify cost drivers and allocate resources effectively. It also helps to identify potential cost optimization measures that can lead to overall project cost reduction.
Preparation and Execution
Preparation and Execution of a Business Case for SAP S/4HANA projects involves a structured approach to ensure a comprehensive and data-driven analysis. The process for creating a Business Case can be broken down into three main stages:
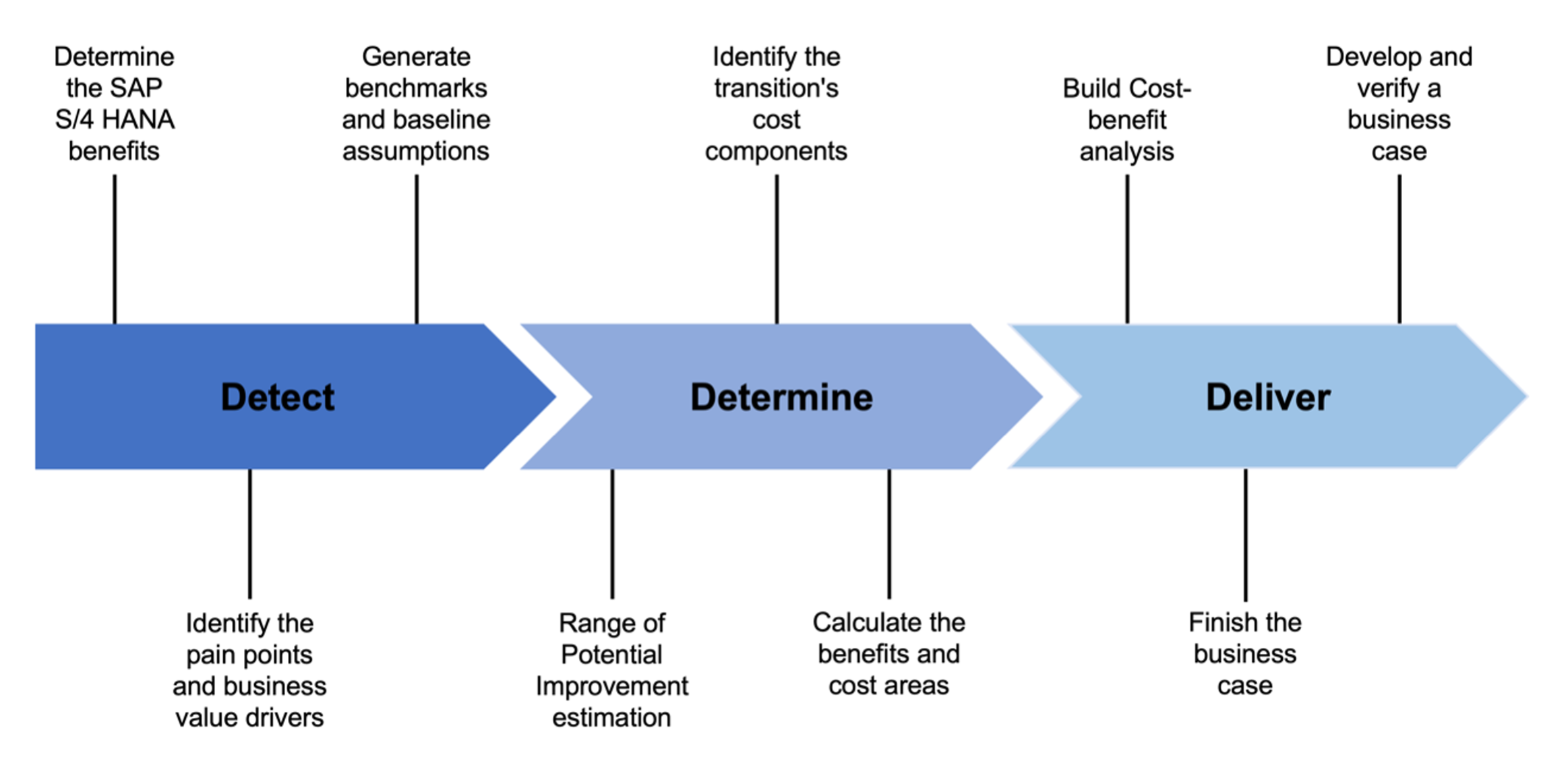
In the first stage, “Detect,” the organization identifies the potential benefits and advantages of adopting SAP S/4HANA. This involves recognizing how SAP S/4HANA can improve business processes, enhance data analytics capabilities, streamline operations, and increase overall efficiency. Additionally, the organization identifies existing pain points and business value drivers to understand the challenges in the current systems and processes. By pinpointing the specific areas where SAP S/4HANA can bring the most significant value and impact, the organization can lay the groundwork for a compelling business case. Furthermore, relevant data is gathered and benchmarks are established to compare the current state of operations with the expected outcomes after SAP S/4HANA implementation. Baseline assumptions for key performance indicators are set to measure the project’s success.
In the second stage, “Determine,” the organization evaluates the potential improvements and benefits that SAP S/4HANA can bring. This evaluation includes estimating the impact on productivity, cost savings, revenue growth, and customer satisfaction. Simultaneously, the costs associated with the transition to SAP S/4HANA are identified, encompassing one-off costs, running costs, and other related expenses. Quantifying the financial benefits and potential cost savings from SAP S/4HANA implementation is essential to weigh against the identified cost areas and assess the overall financial impact.
Finally, in the “Deliver” stage, the organization builds a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis based on the data and calculations from the previous stages. This analysis presents the financial gains and costs associated with the SAP S/4HANA project, providing decision-makers with valuable insights. The findings and information from all previous stages are compiled into a detailed and well-structured business case document. This document articulates the rationale for the project, outlines the expected benefits, and provides a clear financial analysis, ensuring transparency and clarity for stakeholders. Collaboration with relevant stakeholders is crucial during this stage to validate the business case and ensure its alignment with organizational goals. Addressing concerns and incorporating feedback strengthens the credibility and support for the proposed SAP S/4HANA implementation.
Realistic Assessment and Cost Optimization
Evaluating project feasibility considers technical capabilities, resources, timelines, and risks. This aids in setting expectations and aligning with goals. Cost-effectiveness is vital in SAP S/4HANA projects, achieved through process streamlining, resource optimization, and cloud solutions. Comprehensive training and change management enhance workforce efficiency and productivity.
Strategic planning and cost-efficiency maximize SAP S/4HANA benefits. Integration optimizes operations, data analytics, and processes, positioning businesses as innovative leaders. Embracing SAP S/4HANA’s potential fosters adaptation, flourishing, and transformative outcomes in a dynamic digital era.
Technological Advancements and Employer Branding in SAP S/4HANA Adoption
Technical Implementation and the Cloud Approach are crucial for SAP S/4HANA adoption and impact employer branding, especially for young professionals. Implementing SAP S/4HANA involves deploying, configuring, and training a skilled workforce in areas like data migration and system customization. The cloud approach offers cost-effective, flexible solutions with easy access and collaboration benefits.
SAP S/4HANA and Cloud IT adoption boosts operational efficiency and employer branding. Modern systems attract young talent and show innovation and adaptability. Highlighting these technologies in branding showcases a tech-savvy, forward-thinking workplace that resonates with young employees’ preferences for learning and innovation. Demonstrating commitment to employees’ success improves job satisfaction and retention, making the organization more appealing in the competitive job market.
Quantitative and Qualitative Aspects
Quantitative and Qualitative Aspects are essential dimensions to consider when evaluating the impact of SAP S/4HANA adoption. The assessment of both quantitative benefits and financial metrics, alongside qualitative aspects and non-financial advantages, provides a comprehensive understanding of the project’s success and overall value.
Evaluating quantitative benefits and financial metrics involves analyzing measurable outcomes directly related to financial gains and cost savings. These metrics could include improvements in operational efficiency, increased revenue generation, reduced processing time, and enhanced customer satisfaction. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are established to track the project’s progress and measure its success against predetermined targets.
Additionally, organizations must consider the return on investment (ROI) and the payback period to assess the project’s financial viability. Calculating ROI involves comparing the net benefits derived from the SAP S/4HANA implementation with the initial investment. A shorter payback period indicates a faster recovery of the investment, enhancing the project’s attractiveness from a financial standpoint.
On the other hand, qualitative aspects and non-financial advantages capture the broader impacts of SAP S/4HANA adoption that may not be directly quantifiable in monetary terms. These could include improved data accuracy and visibility, enhanced decision-making processes, better compliance and risk management, and increased adaptability to market changes. Qualitative aspects also encompass the cultural and organizational changes that come with technology adoption, such as increased employee engagement and collaboration, a culture of innovation, and improved cross-functional communication.
Assessing both quantitative and qualitative aspects allows organizations to have a holistic view of the SAP S/4HANA project’s overall impact. While financial metrics provide concrete data to justify the investment, qualitative aspects shed light on intangible benefits that contribute to the organization’s long-term success and competitiveness.
Navigating the Path to SAP S/4HANA Success: Unleashing Transformative Outcomes
While Business Cases serve as a solid foundation for successful SAP S/4HANA projects, it is important to acknowledge that they are not the sole key to success. Despite thorough evaluation and strategic planning, unforeseen events and external factors can impact project outcomes. Business Cases are based on the present, and they cannot fully account for future uncertainties or changes in the business landscape.
The successful implementation of SAP S/4HANA requires continuous monitoring, adaptability, and proactive management throughout the project lifecycle. It is crucial for organizations to remain agile and responsive to evolving circumstances, market dynamics, and technological advancements. Post-implementation, organizations must continuously evaluate the effectiveness of SAP S/4HANA and make necessary adjustments to optimize its benefits. This includes ongoing training and development for employees, continuous improvement initiatives, and a commitment to embracing innovation. While Business Cases provide a structured approach to decision-making and lay the groundwork for success, organizations must also foster a culture of learning and innovation to fully realize the potential of SAP S/4HANA and stay ahead in the dynamic digital landscape.
In conclusion, Business Cases form an essential part of the SAP S/4HANA project journey, offering valuable insights and strategic direction. However, sustained success requires a combination of well-planned Business Cases, proactive management, and a commitment to continuous improvement to navigate the complexities of digital transformation and thrive in an ever-changing business environment.
If you want to get more information on Business Cases in SAP S/4HANA Projects, feel free to contact Fabian Winckler (fabian.winckler@www.draxingerlentz.de)